Gastric Balloon in Baltimore, Maryland
Gastric Balloon Procedure in Maryland
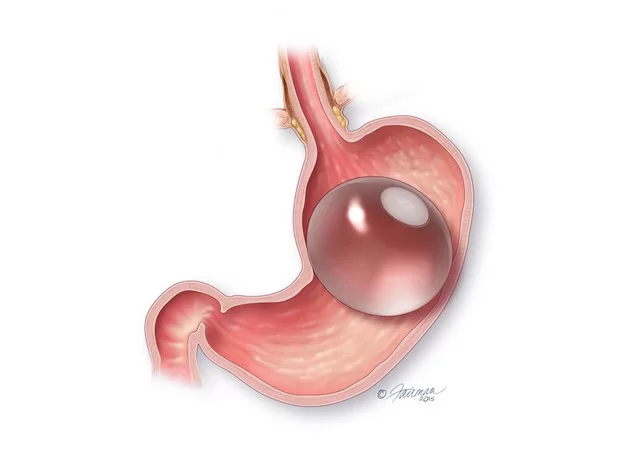
The gastric balloon is a noninvasive weight-loss procedure for those who have failed to lose weight with diet and exercise. Patients considering a Gastric Balloon in Baltimore, Maryland, may find this option beneficial. An endoscope, which is sent down the neck and into the stomach, is used to put a soft gastric balloon in the stomach. As a result, no incisions are required for this surgery. The balloon is then filled with sterile water, which takes up a lot of room in the stomach. The balloon remains in place for 6 months and serves to restrict how much you can safely consume at one time. This is supplemented by frequent consultations with a nutritionist both before and after the balloon to focus on losing and maintaining weight reduction.
An intragastric balloon may be an option for you if:
-
You are ready and willing to commit to healthy living choices, frequent medical checkups, and changing your eating behavior.
- You have never undergone stomach or esophageal surgery.
This program includes a one-year coaching program to assist you in maintaining your new, healthier lifestyle.
If you are interested in the Gastric Balloon treatment in Baltimore, Maryland, please contact Dr. Swift.
Advantages of the Gastric Balloon Procedure in Baltimore, MD
- The gastric balloon can be removed.
- The mortality rate is low.
- Normal GI tract continuity is preserved.
- The absence of incisions results in less operation discomfort and a faster return to regular activities.
- Nutritional deficits are less likely to occur.
- There is no danger of a marginal ulcer.
- There is no danger of the band gadget malfunctioning.
- Possible in individuals who are contraindicated to surgical methods.