Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch in Baltimore, Maryland
The Duodenal Switch is for people who are extremely obese (BMI of 50 or higher) or who have poorly controlled diabetes. The Switch involves both restrictive and malabsorptive components to produce long-term weight loss and improved control of blood sugar. In the restrictive portion of this procedure, the surgeon removes a large portion of your stomach. The new, smaller stomach is about the size of a banana, which limits the amount of food you can eat at once and helps you feel fuller after smaller meals.With the malabsorption portion, the path of your intestines is changed, which allows food to bypass part of the small intestine so you absorb fewer calories, carbohydrates and fat from the foods you eat, helping you lose weight. You will still need to commit to a healthy diet and active lifestyle if you want to maintain weight loss with this procedure. Since you cannot absorb vitamins and nutrients the same way you do before surgery, it is important to take supplements for the rest of your life
The Procedure
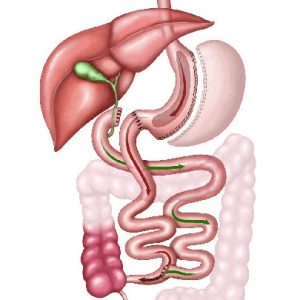
The duodenal switch works because the newly created stomach pouch is smaller and can only hold a few ounces of food at a time, which translates into fewer calories consumed. There is less digestion of food by the smaller stomach pouch, and the segment of small intestine that would normally absorb calories as well as nutrients no longer has food going through it, so there is less absorption of calories and nutrients. Most importantly, the rerouting of the digestive process produces changes in gut hormones that promote satiety, suppress hunger, and reverse one of the primary mechanisms by which obesity induces type 2 diabetes.
Duodenal Switch surgery in Baltimore, Maryland can be performed as a laparoscopic or robotic (minimally invasive) procedure which involves the use of a small telescope-like camera inserted through a small incision made in the abdomen, or as an open procedure where a large midline incision is made in the abdomen. The robotic method is the most commonly used by Dr Swift in Baltimore, Maryland.
Advantages
- Low mortality rate (0.2%)
- Weight loss of 80-90% of pre-operative excess weight within one year
- Overall improved health
- Highest rates of resolution or elimination of co-morbidities such as type II diabetes, sleep apnea, hypertension and many others
What You Need to Know About BPD-DS Surgery
Although Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch Surgery has certain considerations, it is important to consider them alongside its potential benefits. All bariatric surgeries report a risk of staple line leaks, which can be a serious complication and may require revision surgery. While vitamin deficiencies or anemia are possible, these concerns can be mitigated through diligent monitoring and supplementation. Although there is a potential for obstruction of the gastrointestinal tract and the occurrence of frequent diarrhea and malodorous gas, these issues can be effectively addressed through medical intervention. Furthermore, while there is a risk of dumping syndrome, lifestyle adjustments can significantly reduce its impact. It is worth noting that the procedure requires strict adherence to dietary recommendations, lifelong vitamin/mineral supplementation, and regular follow-up visits. These are crucial for successful weight loss outcomes.
Reflux/GERD Prevention Following BPD-DS Surgery
Prior to bariatric surgery, morbidly obese people had a greater incidence of reflux symptoms than the normal population. To reduce the risk of major GERD following bariatric surgery, we regularly examine patients for reflux and hiatal hernia symptoms.
If it is discovered, it is repaired during the bariatric treatment. This technique reduces the danger of delayed surgery for this disease, which may be required in around 20% of patients, and dramatically improves their quality of life following bariatric surgery.
How We Prevent Gallbladder Disease
Morbidly obese people have a greater prevalence of Gallbladder disease than the normal population, both before and after bariatric surgery. In 30-40% of individuals, asymptomatic gall stones might induce acute inflammation and considerable weight loss following bariatric surgery. We carefully evaluate patients for gallbladder abnormalities before to surgery, and if anything is found (gall stones, chronic cholecystitis related to dyskinesia, cholesterol polyps), gallbladder removal during the primary bariatric operation may be suggested. As a result, the likelihood of a subsequent gall bladder operation is reduced. If no gallbladder abnormalities are discovered, patients receive treatment with Ursodiol or Actigall for the first six months following surgery.