Upper Endoscopy Baltimore: GERD/Reflux Procedures in Maryland
It is performed to diagnose the causes of pain, bleeding, or blockage of the upper GI system, and it allows the option of removal of small benign tumors and tissue biopsy. Conditions such as Crohn’s disease and irritable bowel syndrome can also be diagnosed and treated with upper endoscopy. Newer techniques and instruments allow physicians to alter the width of the intestinal tube in cases of narrowing due to scar tissue or reduction of the size of the lumen or stoma, as is the case with bariatric surgery.
Serving cities such as Frederick and Columbia and the counties of Anne Arundel, Maryland, and Lancaster, PA, gastroenterology specialists and Dr. Swift are highly trained in endoscopic technology. Please request an appointment online with Dr. Averbach or Dr. Hamdallah or call their office at 667-234-8725.
Benefits of Upper Endoscopy for GERD/Reflux
The benefits of upper endoscopy for GERD/reflux are numerous and impactful:
- Accurate Diagnosis: Upper endoscopy allows physicians to precisely diagnose the causes of GERD and reflux, which is crucial for effective treatment.
- Minimally Invasive: As a minimally invasive procedure, upper endoscopy does not require any incisions, reducing the risk and discomfort associated with surgery.
- Quick Recovery: Patients typically experience a short recovery time and can return to their normal activities within a few hours after the procedure.
- Effective Treatment: Upper endoscopy can treat various conditions related to GERD and reflux by removing small benign tumors, taking tissue biopsies, and altering the width of the intestinal tube.
- Reduced Risk of Complications: By addressing the underlying causes of GERD and reflux, upper endoscopy helps reduce the risk of complications such as esophageal cancer and strictures.
- Improved Patient Experience: The procedure can enhance patient experience scores by providing accurate diagnoses and effective treatments, leading to better health outcomes and reduced out-of-pocket expenses.
- Health Insurance Coverage: Upper endoscopy is typically covered by most health insurance plans, making it an accessible option for many patients.
Performed by board-certified GI doctors who specialize in GI procedures, upper endoscopy ensures high-quality care. These physicians exceed national benchmarks for quality in colonoscopy and other GI procedures, ensuring patients receive the best possible treatment. Additionally, upper endoscopy can play a role in boosting colon cancer screenings and lowering colon cancer rates by identifying and treating conditions that may increase the risk of colorectal cancer.
Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication (TIF)
Another procedure designed to repair the valve mechanism is called a Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication, or TIF, and is sometimes combined with a hiatal hernia repair if the hernia is greater than 2 cm in length. This procedure consists of an endoscopy where a camera is passed down the throat. A device attached to the endoscope is then used to fold the top portion of the stomach over the bottom of the esophagus to recreate the valve. The rates of reflux resolution are similar to those seen with more traditional fundoplication methods.
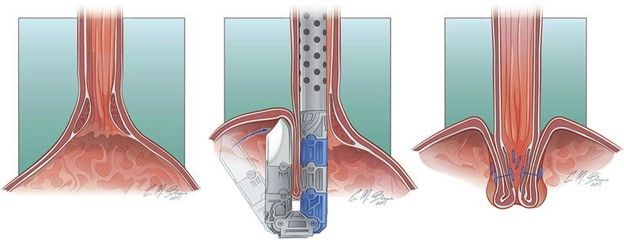
A TIF may be an option for you if:
- You have significant reflux that is not responsive to medication therapy
- Have a small to medium-sized hiatal hernia
- Have a desire to stop taking your antireflux medication
ADVANTAGES
- Low mortality rate
- If no hiatal hernia is present, then the entire procedure is incisionless, which translates to less downtime and less pain
- Ability to a fix hiatal hernia at the same time if one is present
- The over valve is more physiologically similar to the original valve
- High rates of reflux remission
- Lower rates of gas bloat, dysphagia, and flatulence
DISADVANTAGES
- Not able to be performed on patients who have had previous bariatric surgery
- Possibility of recurrence
- Foods that you eat now may cause discomfort, nausea, or vomiting after your surgery
- Requires adherence to dietary recommendations and follow-up compliance
- Only suitable for patients with a BMI less than 40
- A newer procedure, so less data is available on long-term outcomes
Stretta
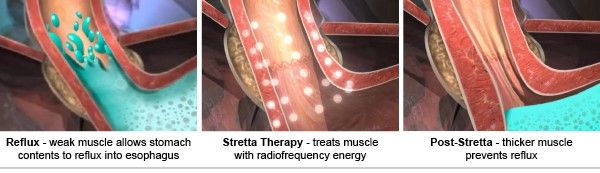
STRETTA may be an option for you if:
- You have significant reflux that is not responsive to medication therapy
- Have a hiatal hernia less than 2cm in length
- Have a desire to stop taking your antireflux medication
ADVANTAGES
- Low mortality rate
- It can be performed on patients who have had previous bariatric surgery, regardless of the procedure
- The entire procedure is incisionless, which translates to less downtime and less pain
- High rates of reflux remission
- Done as an outpatient procedure
- Ability to do multiple treatments if necessary
The Upper Endoscopy Procedure
During the procedure, a thin scope that has a light with a camera located on the tip will be used to look at your digestive tract. The doctor will look at your esophagus, stomach, and duodenum.
An upper endoscopy is typically performed as an outpatient procedure, though there are instances where it may need to be done in a hospital or emergency room setting. This typically happens when your doctor needs to both identify and treat conditions immediately, such as upper digestive bleeding or other digestive diseases.
An endoscopy is often used to identify the causes of symptoms such as:
- Abdominal or chest pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Heartburn
- Bleeding
- Swallowing problems
They can also be helpful in the identification of conditions like inflammation, ulcers, and tumors.
Undergoing an upper endoscopy in Baltimore, Maryland, is a more precise method for identifying abnormal growths and inspecting the interior of your upper digestive system compared to X-rays. If an abnormality is found, it may be possible to treat it through the endoscope. Some abnormalities that can be treated this way include:
- Polyps, which are tissue growths in the stomach, can be detected and removed, and tissue samples can be collected for analysis.
- Restricted sections or strictures in the esophagus, stomach, or duodenum that are the result of cancer or other diseases can be widened or expanded using balloons or other apparatus. In certain instances, a stent could be inserted into the stricture to keep it open.
- Foreign objects lodged in your esophagus can be extracted.
- They can treat bleeding from ulcers, cancer, or varices.
How Do I Prepare for Upper Endoscopy?
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant, have a lung or heart condition, or if you are allergic to any medications before undergoing an upper endoscopy.
Also, tell your doctor if you have:
- Ever been told you need to take antibiotics before a dental or surgical procedure
- Ever had endocarditis (an infection of the heart valves)
- An artificial heart valve
- Rheumatic heart disease
If you have any of these conditions or devices, you may need to take antibiotics before the upper endoscopy.
Do not eat or drink anything for eight hours before the procedure.
If you take medications for conditions such as high blood pressure, thyroid diseases, or a heart condition, you will be able to take them with a sip of water before the procedure. If you have diabetes and use insulin, you will need to adjust the insulin dosage on the day of the procedure. Make sure you consult with your diabetes care provider before doing so. Remember to have your diabetes medication with you to take when the procedure is complete.
It is important to arrange for someone to drive you home after the upper endoscopy, as the sedation used during the procedure can cause drowsiness, dizziness, and impaired judgment. It will make it unsafe for you to drive or operate machinery for up to eight hours following the procedure.
Risks
There is a small chance of a hole (perforation) in the stomach, duodenum, or esophagus from the scope moving through these areas. There is also a small risk of bleeding at the biopsy site.
You could have a reaction to the medicine used during the procedure, which could cause:
- Apnea (not breathing)
- Difficulty breathing (respiratory depression)
- Excessive sweating
- Low blood pressure (hypotension)
- Slow heartbeat (bradycardia)
- Spasm of the larynx (laryngospasm)