Navigating GLP-1 Diabetes and Weight Loss Drug Side Effects
While GLP-1 receptor agonists have gained popularity for weight loss and diabetes management, their benefits often come at the cost of significant risks and limitations. These medications rely on prolonged use to maintain results, leaving many individuals grappling with dependency, side effects, or diminishing effectiveness over time.
Bariatric surgery, by contrast, provides a proven, lasting solution to obesity and its complications. By addressing the root causes of weight gain, surgery offers a safe, effective, and comprehensive approach to sustainable weight loss and long-term health improvement. This blog covers the common and rare side effects of GLP-1 diabetes and weight loss drugs, plus tips on managing them and knowing when to seek help.
Key Takeaways
- GLP-1 receptor agonists can cause dependency and unpleasant side effects like nausea and vomiting.
- Serious risks include thyroid tumors and pancreatitis, requiring close monitoring.
- Bariatric surgery offers lasting weight loss and metabolic health improvements without ongoing medication.
Understanding GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
GLP-1 receptor agonists have revolutionized the treatment of Type 2 diabetes and obesity by mimicking the effects of the natural hormone GLP-1. First approved by the FDA in 2005 with exenatide, these medications enhance insulin production post-meals, aiding in blood sugar control.
They also promote weight loss by suppressing appetite and slowing gastric emptying, making patients feel fuller longer. Now used for obesity treatment without diabetes, GLP-1 receptor agonists are available in various forms, including injectable options like exenatide extended-release. This variety allows healthcare providers to tailor treatments to individual patient needs.
Despite their short-term benefits, GLP-1 medications come with significant drawbacks. They often require continuous use to maintain weight loss, making them a lifelong commitment rather than a definitive solution. Additionally, these drugs may not address the root causes of obesity, leaving patients reliant on medications with no permanent resolution to their condition.
Bariatric surgery, on the other hand, goes beyond symptom management. It permanently alters the digestive system to reduce appetite and improve metabolic health, offering long-lasting results without the need for ongoing pharmacological support.
Common Side Effects of GLP-1 Drugs
GLP-1 receptor agonists are groundbreaking medications used to manage Type 2 diabetes and facilitate weight loss. By mimicking the natural hormone GLP-1, these drugs help lower blood sugar levels, reduce appetite, and promote significant weight reduction. Despite their effectiveness, they come with a range of potential side effects that can impact patient comfort and adherence to treatment. It is crucial for patients and healthcare providers to understand these side effects to optimize treatment outcomes.
- Gastrointestinal Symptoms: Nausea, Vomiting, Diarrhea, Constipation
- Other Side Effects: Dizziness, Fatigue, Headaches
- Serious Adverse Events: Thyroid C-cell tumors, Acute pancreatitis, Kidney injury
- “Ozempic face” from GLP-1 agonists leads to a gaunt look due to rapid weight loss.
GLP-1 receptor agonists, while effective, come with drawbacks, and they also require long-term use, which can be costly and may not address the root causes of obesity. These side effects can be disruptive, affecting daily activities and adherence to treatment. For individuals experiencing persistent discomfort, bariatric surgery provides an effective alternative. By addressing the underlying causes of obesity, surgery eliminates the need for medications and their associated side effects, helping patients achieve better health outcomes without the constant risk of complications.
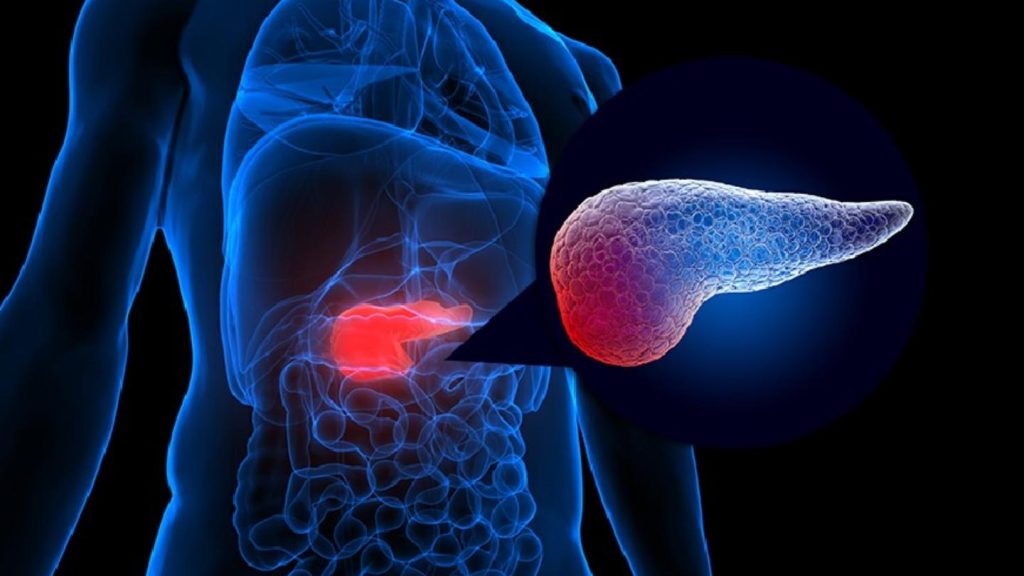
Rare but Serious Adverse Events
GLP-1 receptor agonists are generally safe but can lead to rare serious adverse events. Animal studies indicate a potential risk of thyroid C-cell tumors, raising concerns about medullary thyroid cancer in humans, though clinical trials haven’t confirmed this link. Patients often undergo thyroid screenings as a precaution. Another major concern is acute pancreatitis, causing severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Individuals with risk factors like high triglycerides may be more vulnerable. Immediate medical attention is crucial if symptoms appear.
Kidney injury, particularly with exenatide, can occur due to dehydration from severe gastrointestinal side effects like nausea and vomiting. Patients should seek medical advice if experiencing persistent gastrointestinal issues to prevent kidney damage. Regular kidney function assessments are recommended, especially for those with pre-existing kidney disease. Severe vomiting or inability to pass gas requires urgent medical consultation, as these could signal serious underlying conditions needing immediate intervention.
Despite their rarity, these adverse events necessitate vigilant monitoring by healthcare providers. Patients should be educated on recognizing serious side effects and promptly report any unusual or severe reactions during treatment.
While serious complications are rare, the potential for severe adverse events underscores the risks of relying on GLP-1 drugs for weight management. Bariatric surgery offers a safer, more reliable solution with a well-documented safety profile and long-term benefits. Unlike medications, which require ongoing monitoring for risks like pancreatitis or thyroid issues, bariatric procedures are a one-time intervention with a significantly lower risk of life-threatening complications.
Read more: Essential Tips for Reducing Gas After Gastric Sleeve Surgery
Managing Side Effects and When to Seek Help
Although GLP-1 receptor agonists are praised for their effectiveness in promoting weight loss and managing Type 2 diabetes, they come with significant challenges. Many patients experience uncomfortable side effects such as persistent nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, which can severely disrupt daily life. Furthermore, these medications require long-term use to sustain their benefits, leading to dependency and substantial financial costs due to their high price.
While GLP-1 receptor agonists offer advantages for weight loss and diabetes control, they also pose significant risks, including thyroid C-cell tumors, acute pancreatitis, and kidney injury. These serious adverse events require careful monitoring and can cause anxiety for patients. In contrast to bariatric surgery, which addresses root causes and delivers lasting results, GLP-1 drugs provide only temporary solutions, potentially leading to medication reliance. Additionally, their interactions with other medications add complexity to treatment plans, making them less appealing for extended use.
Bariatric surgery, rather than managing ongoing side effects of GLP-1 medications, eliminates the need for these drugs altogether. Surgical options like gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy enhance metabolic function, promote sustained weight loss, and resolve conditions like Type 2 diabetes without the ongoing challenge of medication management.
Impact on Cardiovascular Health
Although GLP-1 receptor agonists have shown some benefits for heart health, like reducing blood pressure and improving cholesterol levels, they come with significant drawbacks that shouldn’t be overlooked. These medications often require long-term use, leading to dependency and potential side effects such as gastrointestinal discomfort, thyroid C-cell tumors, acute pancreatitis, and kidney injury. Moreover, their impact on weight loss and blood sugar management is often temporary, necessitating continuous medication without addressing the root causes of obesity and Type 2 diabetes.
Despite their initial promise, GLP-1 receptor agonists may not provide a sustainable solution for cardiovascular health improvement. The need for ongoing monitoring and the risk of serious adverse events can make these medications a less appealing option for the long-term management of diabetes and obesity-related heart issues.
While GLP-1 receptor agonists may offer some cardiovascular benefits, these effects are comparable to those achieved through bariatric surgery. In fact, bariatric surgery has been shown to significantly reduce the risk of heart disease, improve blood pressure, and enhance lipid profiles—all without the need for lifelong medications.
For individuals seeking a comprehensive approach to managing obesity and its related health concerns, bariatric surgery stands out as a superior option. It delivers lasting results and significantly lowers the risk of life-threatening complications, making it a more reliable choice for achieving long-term health improvements.
Interaction with Other Medications
GLP-1 receptor agonists, while helpful for managing diabetes and promoting weight loss, can complicate treatment plans due to potential interactions with other medications. These interactions may reduce the efficacy of drugs like oral contraceptives and alter the absorption of medications such as digoxin and statins, necessitating careful monitoring and adjustments. This complexity can become burdensome for patients managing multiple health conditions.
Bariatric surgery, on the other hand, offers a straightforward solution by directly addressing the root causes of obesity. It eliminates the need for ongoing medication management and the associated risks of adverse drug interactions. For those looking for a more effective and uncomplicated approach to weight loss and improved metabolic health, bariatric surgery provides a safer and more reliable alternative.
Summary
While GLP-1 receptor agonists offer some benefits in managing Type 2 diabetes and obesity, they come with notable drawbacks, including dependency on medication and a range of side effects, from gastrointestinal discomfort to severe adverse events like thyroid tumors and pancreatitis. These medications often require long-term use without addressing the root causes of obesity, leaving patients dependent on a temporary solution that can be both costly and cumbersome. In contrast, bariatric surgery provides a more definitive and effective solution for those struggling with obesity and related health issues.
At Ascension Saint Agnes Bariatric Surgery, we understand the limitations of GLP-1 receptor agonists and the challenges they present. We offer bariatric surgery for the Baltimore area, delivering lasting results by addressing the underlying causes of weight gain. Our comprehensive approach ensures improved metabolic health and sustainable weight loss without the ongoing burden of medication management. Contact us today to discover how bariatric surgery can revolutionize your health and offer a lasting solution to weight management challenges!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why should I consider bariatric surgery over GLP-1 receptor agonists for weight loss?
Bariatric surgery offers a more permanent solution by addressing the root causes of obesity, unlike GLP-1 receptor agonists, which often require long-term use and come with potential side effects such as gastrointestinal symptoms, thyroid tumors, and kidney injury. Surgery can lead to sustainable weight loss and improved metabolic health without the dependency on medications.
2. What are the long-term benefits of bariatric surgery compared to GLP-1 medications?
Bariatric surgery provides lasting results, significantly reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease, improving blood pressure, and enhancing lipid profiles. It eliminates the need for ongoing medication management and the risk of serious adverse events associated with GLP-1 drugs, such as pancreatitis and thyroid issues.
3. How does bariatric surgery impact diabetes management compare to GLP-1 drugs?
Bariatric surgery can effectively resolve Type 2 diabetes by enhancing insulin sensitivity and reducing the need for diabetes medications. Unlike GLP-1 drugs, which require continuous use, surgery offers a one-time intervention with long-lasting effects on blood sugar control and overall health.